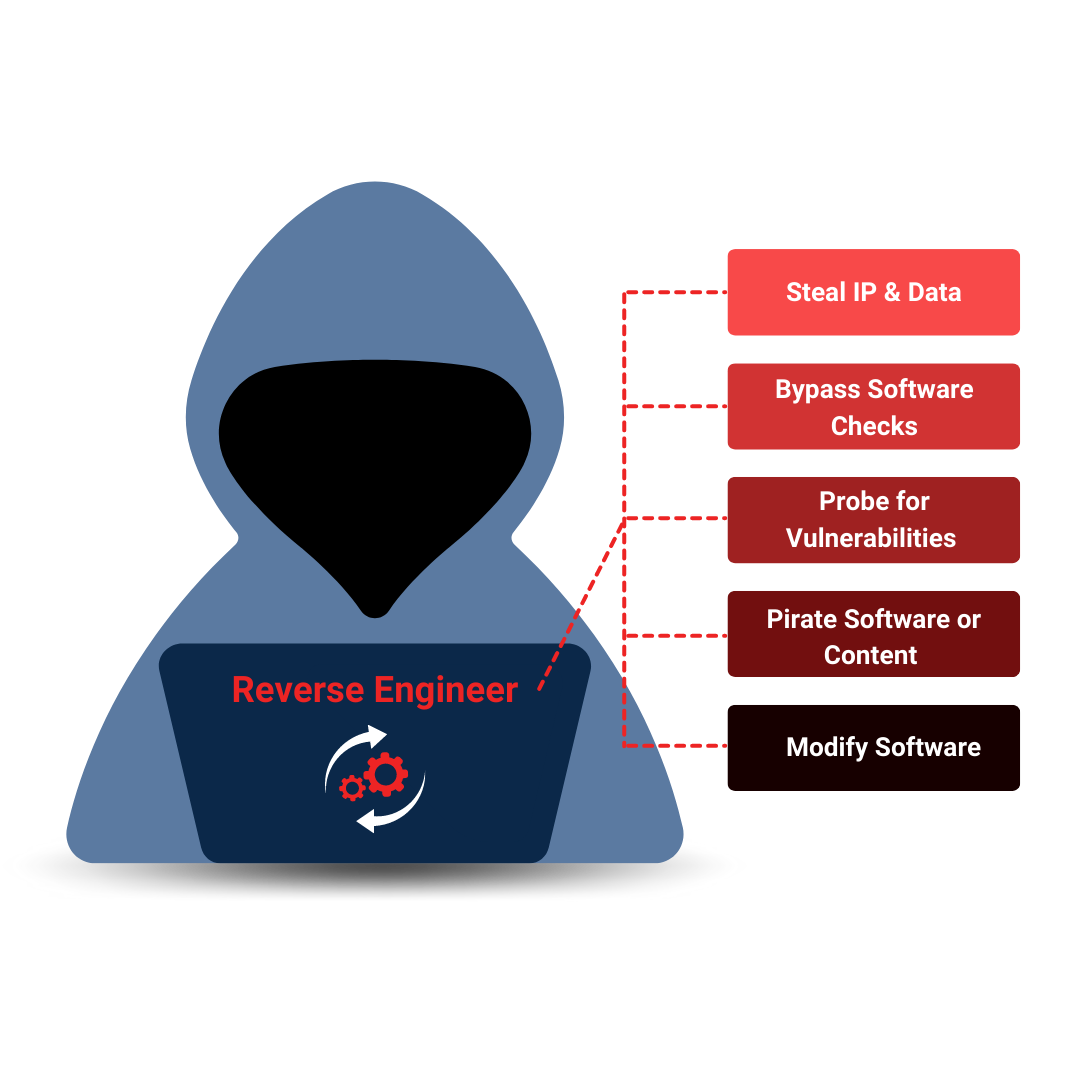
Professional developers know that application security is critical. But with hackers becoming more sophisticated every day, it can be tough to stay ahead of the game. That's where PreEmptive comes in. Our industry-leading app protection software utilizes obfuscation, runtime checks, and more to provide multi-tiered defense against reverse engineering. Rest easy knowing your work is protected!
PreEmptive provides the industry's leading application protection solution, trusted by over 5,000 companies worldwide. With solutions for Java, Android, iOS, .NET, and JavaScript, we offer unparalleled protection for mobile and web applications while ensuring compliance with industry standards.